Science Objective #2
Map SO:SO₂ ratio
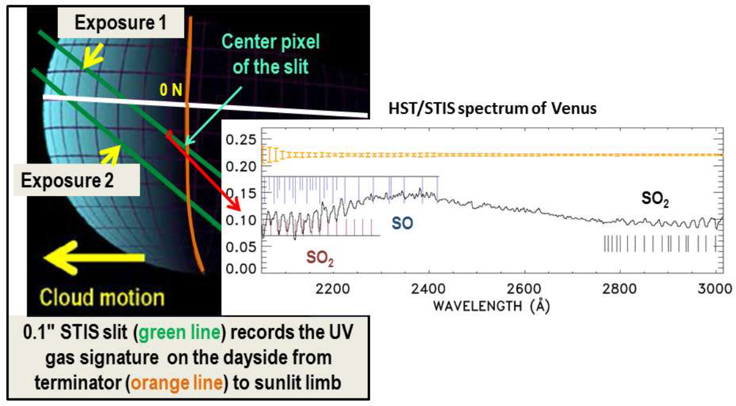
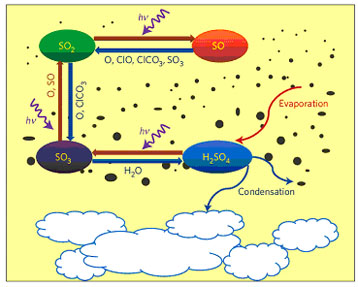
As mentioned previously, the primary sink for SO₂ above the clouds of Venus involves its dissociation by UV sunlight: SO₂ + hν → SO + O. To understand sulfur chemistry better, measuring the SO:SO₂ abundance ratio is crucial. However, the SO absorption spectrum overlaps with the stronger SO₂ absorption band around 220 nm, requiring high spectral resolution to distinguish betwee the two.
Observations using the STIS UV spectrograph on the Hubble Space Telescope found a column abundance ratio of SO:SO₂ averaging 1:10, ranging from 1:4 to 1:25. These measurements are limited due to their sparsity and large error margins (over 50%), making it difficult to determine any correlation with other parameters. Furthermore, colocated SO₂ and SO measurements could reduce uncertainties in SO₂ UV data retrievals, as many studies assumed a constant SO₂ ratio of 1:10, which may not account for the actual variability in this ratio.